What is Commercial Space Flight?
SpaceX’s Starship represents the cutting edge of commercial space flight technology
Commercial space flight refers to space transportation services provided by private companies rather than government agencies. Unlike traditional government-led space programs, commercial space ventures operate on business models that aim to make space access more affordable, reliable, and eventually profitable. This shift represents a fundamental change in how humanity approaches space exploration and utilization.
The significance of commercial space flight in modern aerospace cannot be overstated. It has introduced market competition into what was once an exclusively government domain, driving innovation and cost reduction. Companies like SpaceX have already dramatically lowered launch costs through reusable rocket technology, while others are developing new business models around space tourism, satellite deployment, and even asteroid mining.
Stay Updated on Commercial Space Developments
Get the latest news about launches, technological breakthroughs, and space tourism opportunities delivered to your inbox.
Key Players in Commercial Space Flight
SpaceX: Revolutionizing Space Access

Founded by Elon Musk in 2002, SpaceX has become the most prolific commercial launch provider in the world. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket has transformed the economics of space access through its reusable first stage, which can land back on Earth after delivering payloads to orbit. This innovation alone has slashed launch costs by millions of dollars per mission.
SpaceX’s crown jewel is Starship, a fully reusable super heavy-lift launch vehicle designed to carry both crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Standing at 120 meters tall when paired with its Super Heavy booster, Starship represents the most ambitious spacecraft development program in history. With a payload capacity exceeding 100 metric tons to low Earth orbit, Starship aims to make interplanetary travel economically viable.
Blue Origin: The Steady Approach

Founded by Amazon’s Jeff Bezos in 2000, Blue Origin has taken a methodical approach to space development, embodied in their motto “Gradatim Ferociter” (Step by Step, Ferociously). The company’s New Shepard vehicle has successfully demonstrated suborbital space tourism capabilities, taking paying customers to the edge of space where they experience several minutes of weightlessness.
Blue Origin is also developing New Glenn, a heavy-lift orbital rocket that will compete with SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy. The company’s long-term vision includes building space infrastructure that will allow millions of people to live and work in space, with a focus on utilizing space resources to benefit Earth.
“We’re really at the beginning of a golden age of space exploration. I think it’s going to get us all excited about being out there in space, and then we’re going to see amazing things happen.” – Jeff Bezos, Blue Origin founder
Other Notable Players

While SpaceX and Blue Origin often dominate headlines, several other companies are making significant contributions to commercial space flight:
- Virgin Galactic: Founded by Richard Branson, focusing on suborbital space tourism with its SpaceShipTwo vehicle.
- Rocket Lab: Specializing in small satellite launches with its Electron rocket.
- Sierra Space: Developing the Dream Chaser spaceplane for cargo and eventually crew transport to the ISS.
- Axiom Space: Building the first commercial space station to eventually replace the ISS.
- Boeing: Partnering with NASA on the Starliner spacecraft for crew transport.
- Relativity Space: Using 3D printing technology to manufacture entire rockets.
Technological Advancements Driving Commercial Space Flight

Reusable Rocket Technology
The single most transformative innovation in commercial space flight has been the development of reusable rockets. SpaceX pioneered this approach with its Falcon 9, which can land its first stage either on land or on autonomous drone ships at sea. Blue Origin similarly designed New Shepard from the ground up for reusability. This approach has dramatically reduced launch costs from tens of thousands of dollars per kilogram to just a few thousand.
SpaceX’s Starship takes reusability to the next level by making the entire launch system reusable, not just the first stage. This could potentially reduce costs by another order of magnitude, bringing launch prices down to hundreds of dollars per kilogram – a revolutionary change that would transform the economics of space utilization.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Modern commercial spacecraft benefit from materials and manufacturing techniques that didn’t exist during the early space age. Companies like Relativity Space are 3D printing entire rockets, reducing part counts from thousands to hundreds while enabling rapid iteration and customization. SpaceX’s decision to build Starship from stainless steel rather than carbon fiber represented an innovative approach that balanced cost, manufacturability, and performance.
Download Our Free Guide
Get our comprehensive guide to commercial space flight technology and learn how these innovations are making space more accessible.
Autonomous Systems and AI
Modern commercial spacecraft incorporate sophisticated autonomous systems and artificial intelligence that enable precision landings, automated docking with space stations, and complex mission planning. These technologies reduce the need for human intervention, improving safety and reliability while reducing operational costs.
Current Commercial Space Flight Projects
SpaceX Starship Development

SpaceX’s Starship program has progressed through multiple prototype iterations, with test flights demonstrating increasingly complex capabilities. Recent tests have shown successful launches, controlled descents, and landing attempts. While not all tests have been successful, each provides valuable data that improves the next iteration. The company aims to achieve orbital flight tests soon, followed by lunar missions and eventually Mars landings.
Blue Origin’s New Shepard and Beyond

Blue Origin’s New Shepard vehicle has conducted multiple successful suborbital tourism flights, taking paying customers to the edge of space. The company is also developing its orbital New Glenn rocket, which will compete in the heavy-lift market. Additionally, Blue Origin is working on the Blue Moon lunar lander, which aims to support NASA’s Artemis program for returning humans to the Moon.
Upcoming Commercial Space Missions
| Company | Mission | Vehicle | Target Date | Objective |
| SpaceX | Polaris Dawn | Crew Dragon | 2024 | First commercial spacewalk |
| Axiom Space | Ax-2 | Crew Dragon | 2024 | Private ISS mission |
| Blue Origin | New Glenn Debut | New Glenn | 2024 | First orbital launch |
| SpaceX | dearMoon | Starship | 2025 | Lunar flyby with civilians |
Challenges Facing Commercial Space Flight

Safety Concerns
Despite technological advances, space remains an inherently dangerous environment. Commercial space companies must balance innovation with rigorous safety protocols. The fatal Virgin Galactic crash in 2014 and various test flight failures by other companies highlight the risks involved. Companies are implementing extensive testing regimes, redundant systems, and abort capabilities to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory Hurdles

The regulatory framework for commercial space activities continues to evolve. In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) oversees commercial launches and reentries, while international activities fall under various treaties and agreements. Companies must navigate complex licensing processes, environmental reviews, and safety certifications. Finding the right balance between ensuring public safety and enabling innovation remains a challenge.
Benefits of Commercial Space Flight
- Reduced launch costs through competition
- Accelerated innovation cycle
- New economic opportunities in space
- Increased access for researchers and private citizens
- Development of dual-use technologies
Challenges of Commercial Space Flight
- Safety risks in an inherently dangerous environment
- Complex regulatory landscape
- Environmental concerns about launches
- Space debris management
- High initial capital requirements
Environmental Impact
As launch frequencies increase, the environmental impact of commercial space flight is receiving more scrutiny. Rocket launches produce carbon emissions and other pollutants, though the total impact remains small compared to other industries. Some companies are exploring more environmentally friendly propellants, while others argue that the benefits of space-based solar power and Earth observation for climate monitoring outweigh the environmental costs of launches.
The Emerging Space Tourism Industry
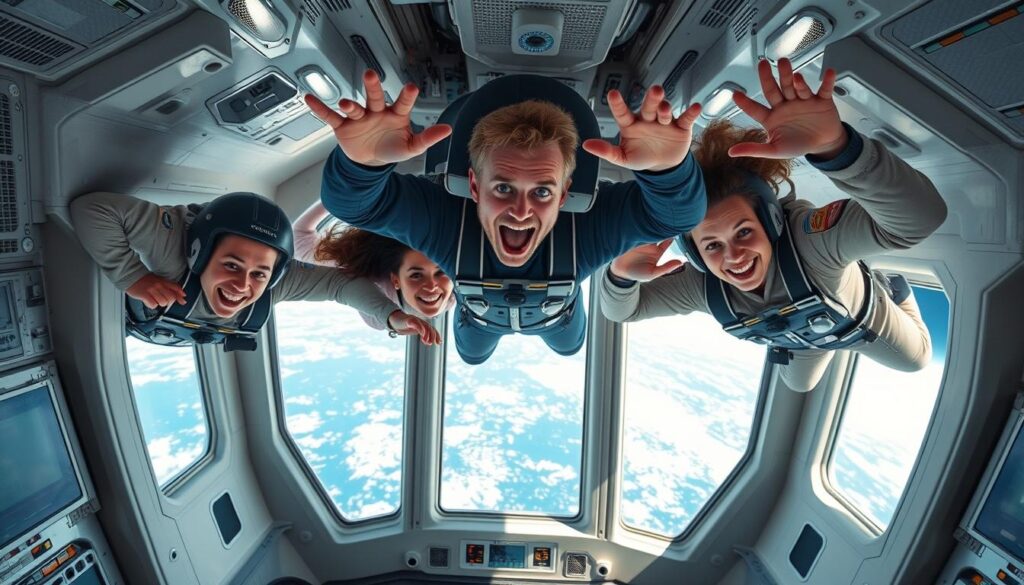

Space tourism represents one of the most visible aspects of commercial space flight. Companies like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic are already offering suborbital flights that provide several minutes of weightlessness and views of Earth from space. SpaceX has taken tourism further with orbital missions like Inspiration4, which sent four civilians on a three-day journey around Earth.
Current Space Tourism Options
- Suborbital Flights: Brief experiences lasting 10-15 minutes, reaching altitudes of 100+ km with several minutes of weightlessness. Offered by Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic for $250,000-$450,000.
- Orbital Tourism: Multi-day missions circling Earth in orbit. SpaceX has conducted private orbital missions with prices estimated at $50-55 million per seat.
- ISS Visits: Stays aboard the International Space Station, typically lasting 1-2 weeks. Arranged through Axiom Space using SpaceX transportation for approximately $55 million.
- Lunar Tourism: Planned missions around the Moon, such as SpaceX’s dearMoon project, scheduled for 2025 (prices undisclosed).
While current prices restrict space tourism to the ultra-wealthy, companies aim to gradually reduce costs through economies of scale and technological improvements. Some analysts predict that suborbital space tourism could become accessible to upper-middle-class consumers within the next decade, with prices potentially dropping below $50,000 per flight.
The Future of Commercial Space Flight
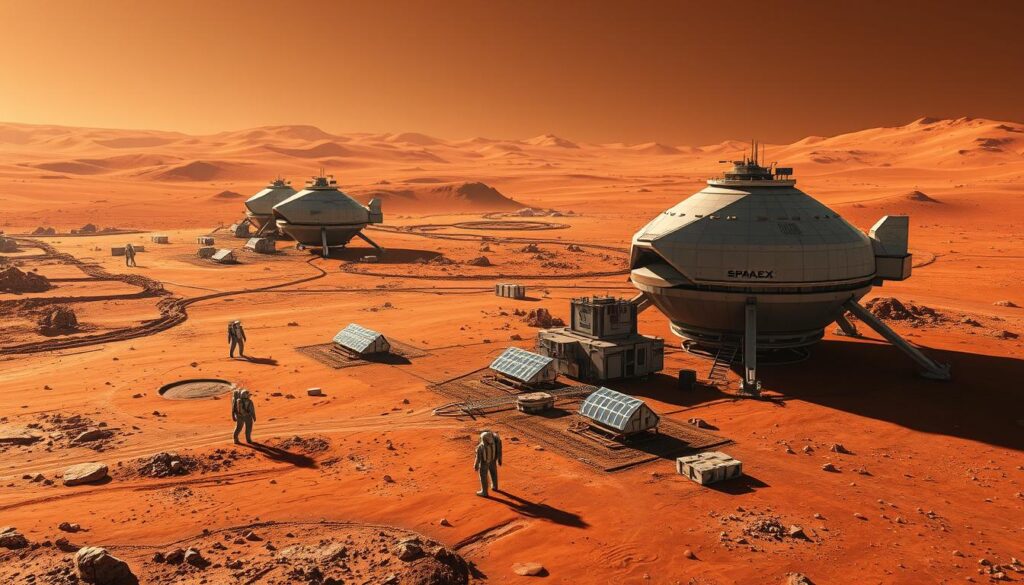

Lunar and Mars Ambitions
By 2030, commercial space flight could extend regularly to the Moon and potentially Mars. SpaceX’s Starship is explicitly designed for Mars colonization, while Blue Origin has expressed interest in developing lunar infrastructure. NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon, heavily leverages commercial partnerships. These missions will likely combine government funding with commercial capabilities.
Space-Based Economy
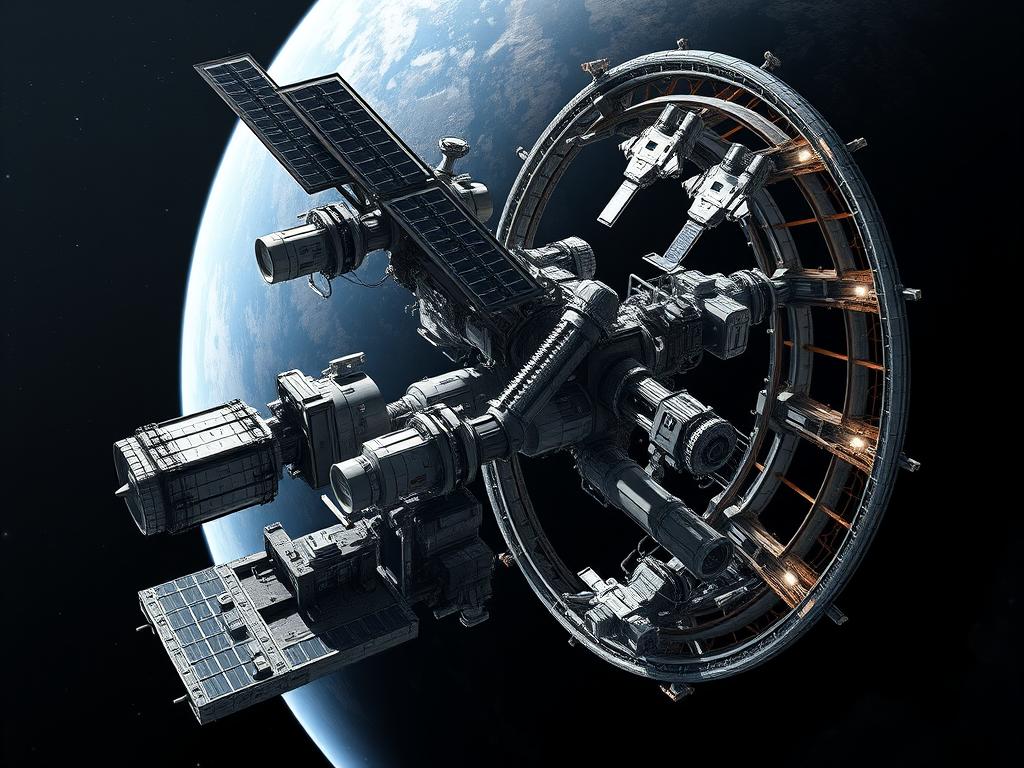

Beyond tourism and exploration, commercial space flight is enabling an entirely new space-based economy. Companies are developing capabilities for in-space manufacturing, taking advantage of microgravity to produce materials impossible to create on Earth. Others are exploring asteroid mining for rare metals or developing space-based solar power. These ventures could potentially generate trillions of dollars in economic activity while helping solve resource constraints on Earth.
Democratization of Space Access
Perhaps the most profound impact of commercial space flight will be the democratization of space access. As launch costs continue to fall, more countries, companies, universities, and even individuals will be able to conduct space activities. This could lead to an explosion of innovation similar to what occurred with the internet, as new applications for space-based services emerge from a diverse global community.
How much does it cost to go to space as a tourist?
Current prices vary by experience. Suborbital flights with Blue Origin or Virgin Galactic cost between $250,000-$450,000 per person. Orbital missions with SpaceX cost approximately $50-55 million per seat. Prices are expected to decrease as technology matures and operations scale up.
When will SpaceX send humans to Mars?
Elon Musk has stated that SpaceX aims to send the first humans to Mars by the late 2020s, with more substantial settlement efforts in the 2030s. However, these timelines are aspirational and subject to technological development, funding, and regulatory approval.
Is commercial space flight safe?
Commercial space flight carries inherent risks, as all spaceflight does. Companies implement extensive safety systems and testing protocols, but the environment remains challenging. Current commercial vehicles have strong safety records, though the industry is still maturing. All passengers must acknowledge and accept certain risks.
Conclusion: A New Era of Space Exploration

Commercial space flight represents one of the most significant shifts in how humanity approaches space exploration and utilization. By introducing market forces and private innovation into what was once exclusively a government domain, companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have accelerated progress and expanded possibilities. The coming decades will likely see space become increasingly integrated into our economy and society.
While challenges remain in terms of safety, regulation, and environmental impact, the trajectory is clear: space is becoming more accessible, more useful, and more important to our future. Whether through tourism that changes perspectives, manufacturing that creates new materials, or eventual settlement that expands human presence beyond Earth, commercial space flight is opening doors that once seemed firmly closed.
Stay Connected with Space Developments
Join our community of space enthusiasts to receive updates on launches, breakthroughs, and opportunities in commercial space flight.




телевизор sharp aquos ремонт дом ремонт телевизор шарп