Understanding Silent Heart Disease
Silent heart disease refers to cardiovascular conditions that develop with minimal or easily overlooked symptoms. Unlike the dramatic chest clutching portrayed in movies, real heart problems often manifest in subtle ways. According to research, up to 45% of heart attacks are “silent,” meaning they occur without the classic symptoms most people associate with cardiac events.
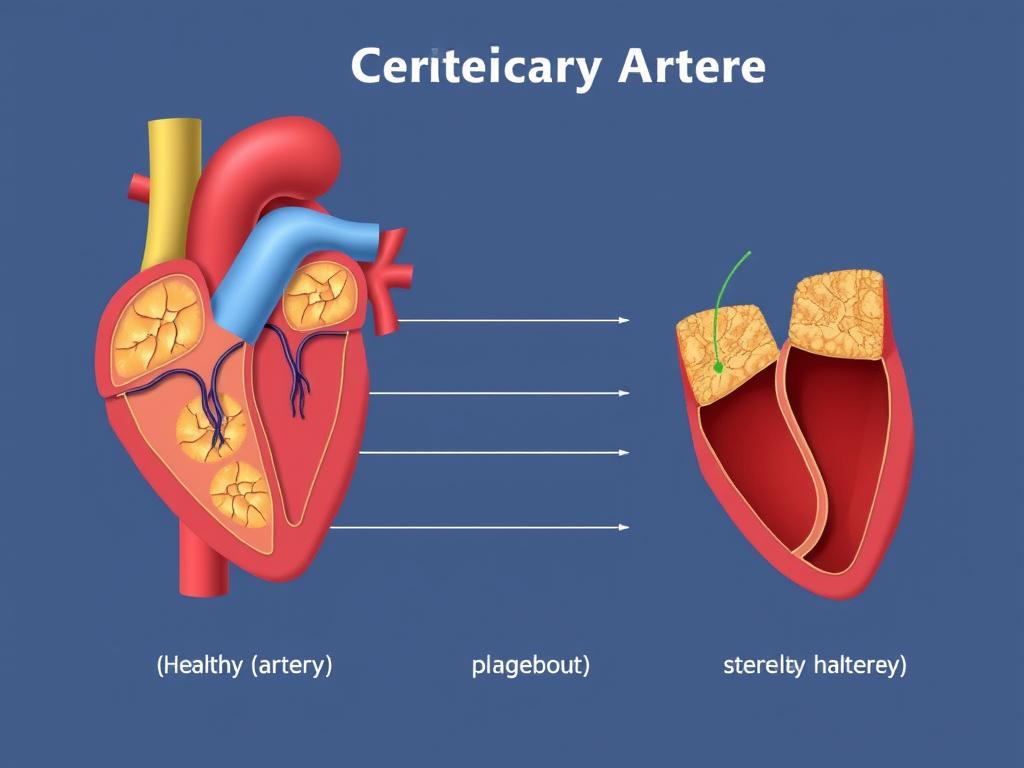
These silent symptoms can indicate coronary artery disease, where plaque builds up in your arteries, restricting blood flow to your heart. When left undetected, this condition can lead to heart attacks, heart failure, or even sudden cardiac death. Early recognition of these warning signs can lead to timely intervention and potentially save your life.
1. Unusual Fatigue
Feeling more tired than usual might seem like a normal part of aging or a busy lifestyle. However, persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest can be one of the silent symptoms of heart disease. When your heart can’t pump blood efficiently, your muscles receive less oxygen, leading to unusual exhaustion.
Why It’s Often Missed
Many people attribute fatigue to stress, poor sleep, or simply “getting older.” Women, in particular, report fatigue as a primary symptom before heart attacks, yet it’s frequently overlooked by both patients and healthcare providers.
When to Seek Help
If you experience new or worsening fatigue that persists for more than a few days, especially if it occurs with minimal exertion or interferes with daily activities, consult your doctor. This is particularly important if you have other risk factors for heart disease.

2. Shortness of Breath
Finding yourself winded after climbing stairs or during light activities that never troubled you before could signal heart problems. When your heart can’t pump efficiently, blood can back up in the pulmonary veins, causing fluid to leak into the lungs and making breathing difficult.
Why It’s Often Missed
Many people attribute breathlessness to aging, weight gain, or being “out of shape.” It’s easy to gradually adjust to declining stamina without realizing something serious might be happening.
When to Seek Help
If you notice a significant change in your breathing capacity, especially when lying down or during minimal exertion, don’t wait to get it checked. Shortness of breath that comes on suddenly or wakes you from sleep warrants immediate medical attention.
3. Jaw, Neck, or Back Pain
Heart disease can cause pain that radiates to your jaw, neck, or upper back. This happens because pain signals from the heart travel along the same nerve pathways as these areas. Women, in particular, often experience these symptoms rather than classic chest pain.
Why It’s Often Missed
These pains are frequently mistaken for dental problems, muscle strain, arthritis, or stress. Without accompanying chest discomfort, few people connect these symptoms to heart issues.
When to Seek Help
If you experience unexplained pain in your jaw, neck, or upper back—especially if it comes and goes or worsens with exertion—consult a healthcare provider. Be particularly vigilant if the pain occurs alongside other symptoms on this list.

4. Irregular Heartbeat or Palpitations
Occasional heart flutters are common and often harmless. However, frequent palpitations, a racing heartbeat, or irregular rhythm could indicate arrhythmias related to heart disease. These rhythm disturbances can occur when heart tissue is damaged or stressed.
Why It’s Often Missed
Many people experience occasional palpitations due to caffeine, stress, or anxiety. This makes it easy to dismiss more serious rhythm problems as just “stress-related” or “normal.”
When to Seek Help
If you notice new or worsening palpitations, especially if they occur frequently, last more than a few seconds, or are accompanied by dizziness or shortness of breath, consult your doctor. Monitoring your pulse can help you identify irregularities.

5. Swelling in Legs, Ankles, or Feet
When your heart isn’t pumping effectively, blood can back up in your veins, causing fluid to accumulate in your tissues. This often appears as swelling (edema) in your lower extremities. While occasional swelling can be normal, persistent or worsening edema could signal heart failure.
Why It’s Often Missed
Many people attribute swelling to aging, standing too long, or salt consumption. The gradual onset often means people adjust to the symptom rather than recognizing it as problematic.
When to Seek Help
If you notice persistent swelling that gets worse throughout the day, leaves indentations when pressed (pitting edema), or doesn’t improve with elevation, consult your doctor. This is especially important if the swelling is accompanied by shortness of breath.
6. Digestive Issues Mistaken for Indigestion
Heart problems can sometimes manifest as digestive discomfort. Symptoms like nausea, stomach pain, or a feeling of fullness or choking can actually be signs of heart disease, particularly in women. These symptoms may worsen with physical activity and improve with rest.
Why It’s Often Missed
These symptoms are almost always attributed to gastrointestinal issues like acid reflux, indigestion, or food intolerance. Few people consider heart disease when experiencing stomach discomfort.
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent digestive symptoms that don’t respond to antacids or dietary changes, especially if they worsen with exertion, consider asking your doctor about possible cardiac causes. This is particularly important if you have risk factors for heart disease.

7. Sleep Disturbances
Sleep apnea and heart disease often go hand in hand. If you wake up gasping for air, snore loudly, or feel excessively tired despite a full night’s sleep, your heart could be involved. Sleep problems can both contribute to and result from heart conditions.
Why It’s Often Missed
Sleep disturbances are frequently attributed to stress, aging, or weight gain. Many people don’t realize that breathing interruptions during sleep can strain the heart and indicate existing cardiovascular issues.
When to Seek Help
If your partner notices you stop breathing during sleep, you wake up gasping, or you feel unrested despite adequate sleep time, discuss these symptoms with your doctor. A sleep study may be recommended to assess for sleep apnea, which can be treated to reduce heart strain.

8. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Feeling dizzy or lightheaded, especially when standing up quickly, could indicate that your heart isn’t pumping enough blood to your brain. This can happen when arteries are narrowed or when the heart’s pumping function is compromised.
Why It’s Often Missed
Dizziness is commonly attributed to dehydration, low blood sugar, inner ear problems, or medication side effects. The intermittent nature of these episodes makes them easy to dismiss.
When to Seek Help
If you experience recurring dizziness without an obvious cause, especially if it’s accompanied by shortness of breath or occurs with exertion, consult your doctor. Sudden, severe dizziness with other symptoms requires emergency attention.
9. Unexplained Sweating
Breaking out in a cold sweat for no apparent reason, particularly if accompanied by any other symptoms on this list, could signal heart problems. This happens because your body goes into “fight or flight” mode when your heart is struggling.
Why It’s Often Missed
Sweating is often attributed to menopause, anxiety, infection, or simply being in a warm environment. Without other obvious cardiac symptoms, few people connect sweating to heart issues.
When to Seek Help
If you experience cold sweats that aren’t related to physical exertion or fever, especially if they occur with discomfort in your chest, arms, or jaw, seek medical attention promptly. Nighttime sweating that soaks your sheets should also be evaluated.

10. Persistent Cough
A chronic cough, especially one that produces white or pink mucus, can be a sign of heart failure. This happens when fluid builds up in the lungs due to the heart’s inability to keep up with the body’s demands.
Why It’s Often Missed
Coughs are almost always attributed to respiratory infections, allergies, or asthma. The connection to heart function is rarely considered, especially in people without known heart disease.
When to Seek Help
If you develop a persistent cough that doesn’t resolve with typical treatments, especially if it’s worse when lying down or accompanied by shortness of breath, consult your doctor. A cough that produces frothy or pink-tinged mucus requires immediate medical attention.

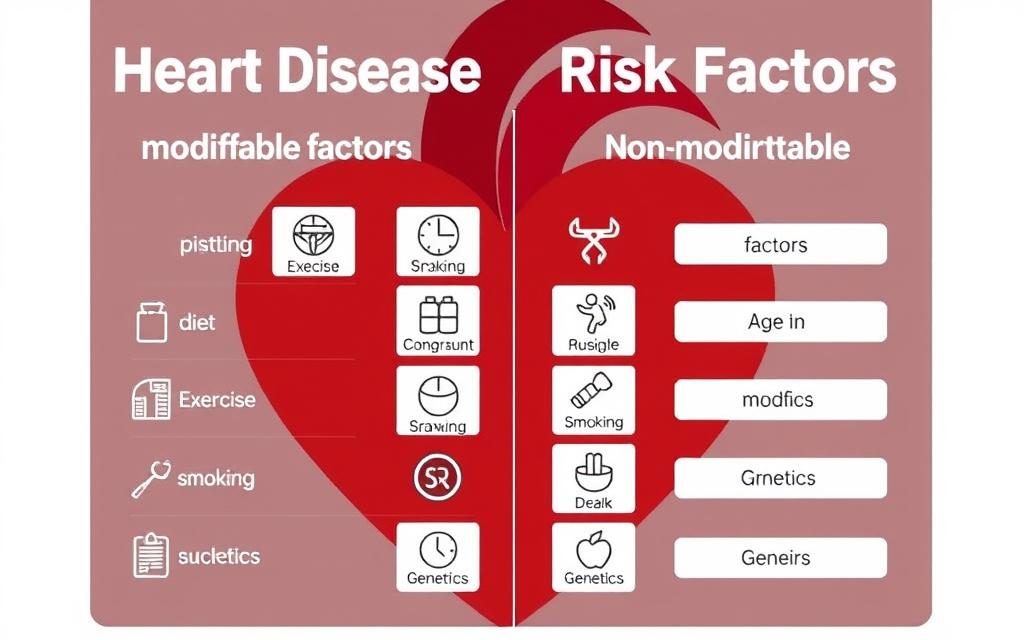
Risk Factors You Should Know
Certain factors increase your risk of developing heart disease. Being aware of these can help you assess your personal risk level and determine how vigilant you should be about potential symptoms.
Modifiable Risk Factors
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- High stress levels
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age (men over 45, women over 55)
- Family history of heart disease
- Gender (men at higher risk, though women’s risk increases after menopause)
- Race (higher risk in African Americans, Mexican Americans, Native Americans)
- History of preeclampsia during pregnancy
Frequently Asked Questions About Silent Heart Disease
How common are silent heart attacks?
Research suggests that up to 45% of all heart attacks are silent, meaning they occur without the classic symptoms most people associate with heart attacks. They’re more common in men than women, though women often experience more subtle symptoms overall.
Can a normal EKG rule out heart disease?
No, a normal electrocardiogram (EKG) doesn’t completely rule out heart disease. Some types of heart problems only show up during physical activity or stress. Additional tests like echocardiograms, stress tests, or cardiac MRIs may be needed to detect certain heart conditions.
What’s the difference between angina and a heart attack?
Angina is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, typically during physical exertion or stress. It usually resolves with rest or medication. A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is completely blocked, causing permanent damage to heart muscle. Angina can be a warning sign of increased heart attack risk.

Don’t Ignore the Warning Signs
Silent symptoms of heart disease can be easy to dismiss or attribute to less serious conditions. However, recognizing these warning signs early and seeking appropriate medical care can literally save your life. Heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide, but many of these deaths are preventable with early intervention.
If you experience any of the symptoms discussed in this article, especially if you have multiple risk factors for heart disease, don’t wait to seek medical attention. Remember that heart disease doesn’t always announce itself with dramatic chest pain—sometimes, the quietest symptoms speak the loudest about your heart’s health.

Don’t Wait Until It’s Too Late
Heart disease symptoms can be subtle but dangerous. If you’re experiencing any of these warning signs, speaking with a cardiologist could save your life.
Know Your Heart Health Status
Understanding your risk factors is the first step toward heart health. A cardiologist can help assess your personal risk and create a prevention plan tailored to your needs.
Take Action for Your Heart Health Today
Don’t wait for symptoms to become severe. Early detection and treatment of heart disease can prevent serious complications and save lives. Speak with a cardiologist about your symptoms and risk factors.
Or call our Heart Health Hotline: 1-800-HEART-HELP